No products added!
Category
Date Posted
February 13, 2024
/
0 Comment
Unraveling the Core Foundation of QMS
Learn about History and Scope of ISO 9001 Standard.
ISO 9001 is an international standard for quality management systems (QMS) developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). It is designed to help organizations of all sizes and industries to consistently provide products and services that meet customer needs and comply with regulations.
ISO 9001:2015 is provides a systematic approach to managing quality, with a focus on identifying and managing risks and opportunities, and continuously improving processes to enhance customer satisfaction and business performance. It is applicable to any organization, regardless of size or industry, and can be used by both product and service-oriented organizations to improve their quality performance, efficiency, and competitiveness.
“ISO 9001:2015: A universal standard for all organizations, regardless of size, industry, or location.”
Versions of ISO 9001 :
The current revision of the ISO 9001 standard is ISO 9001:2015. It was published on September 23, 2015, and is the fifth revision of the ISO 9001 standard. An new requirement to address climate action changes is amended in February 2024. The previous versions of ISO 9001 are,
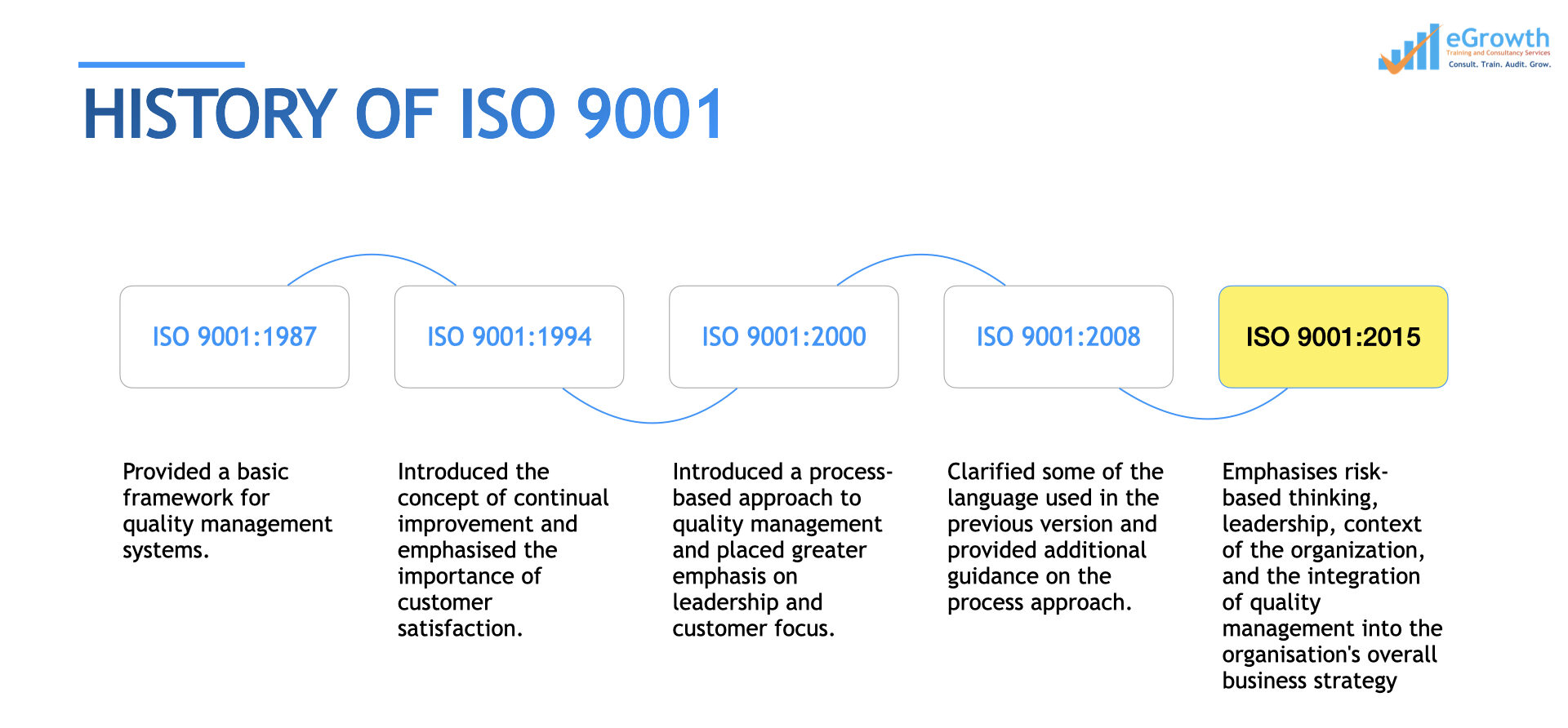
Image: History of ISO 9001 (QMS)
Principles of Quality Management
1. Customer Focus
This principle requires organizations to understand and meet customer requirements and strive to exceed their expectations.
2. Leadership
This principle requires leaders to provide a clear vision and set objectives that are consistent with the organization’s purpose. They should also create and promote a culture of quality and encourage employee participation.
3. Engagement of People
This principle requires that all employees should be engaged in achieving the organization’s objectives and encouraged to contribute to continual improvement.
4. Process Approach
This principle requires that quality management should be a systematic and process-driven approach that considers all the activities involved in delivering a product or service.
5. Improvement
This principle requires organizations to continuously improve their processes, products, and services by implementing corrective actions and preventative measures.
6. Evidence Based Decision Making
This principle requires that Decision making should be based on factual, reliable and validated data and analysis.
7. Relationship Management
This principle requires organizations to establish and maintain positive relationships with their suppliers and other interested parties to enhance their ability to create value.
PDCA Cycle in ISO 9001:2015
The PDCA cycle is a continuous improvement model used in various quality management systems, including ISO 9001:2015. It stands for Plan-Do-Check-Act and is also known as the Deming Cycle, after its creator, Dr. W. Edwards Deming. The PDCA cycle is a fundamental tool in quality management that helps organizations improve their processes and products continually. This cycle can be applied to any process or system, including manufacturing, service delivery, and administrative processes.
The four stages of the PDCA cycle are:
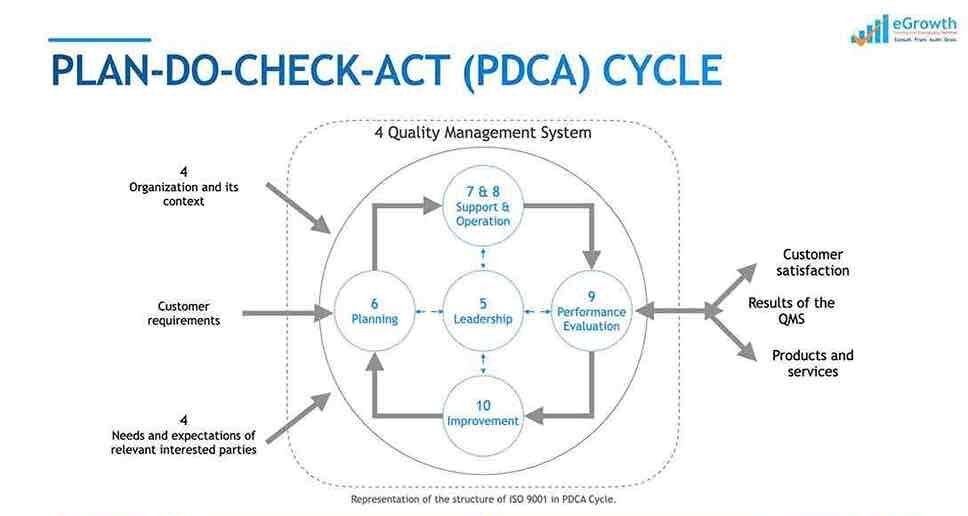
Image: PDCA Cycle
1. Plan (P)
In this stage, the organization identifies the problem, sets goals, and develops a plan to achieve them. The planning stage is critical to the success of the cycle because it sets the foundation for the other stages.
2. Do (D)
In this stage, the organization implements the plan and carries out the activities necessary to achieve the goals set in the planning stage. This is the action phase of the cycle.
3. Check (C)
In this stage, the organization evaluates the results of the activities carried out in the “Do” stage. This evaluation is done using metrics or other forms of measurement to determine if the activities were successful in achieving the goals set in the planning stage.
4. Act (A)
In this stage, the organization takes action based on the results of the evaluation in the “Check” stage. If the goals were met, the organization can implement the changes on a larger scale. If the goals were not met, the organization will revise the plan and start the cycle again.
Conclusion
The PDCA cycle is a continuous process that organizations can use to improve their processes and products continually. Each cycle builds on the previous one, and the organization continues to refine and improve its processes over time.
References
- Book by eGrowth – Mastering Implementation of ISO 9001
- Refer Course Menu for various training related to ISO 9001 or Quality Management
ISO 9001 is notaone-size-fits-allsolution;rather, it provides a flexible framework that can be adapted to various industries and organisational sizes.
Tags :
261



